Understanding Smart Contracts: How They Work
In the world of technology, smart contracts have been gaining popularity for their ability to automate and execute agreements without the need for intermediaries. But what exactly are smart contracts and how do they work?
What are Smart Contracts?
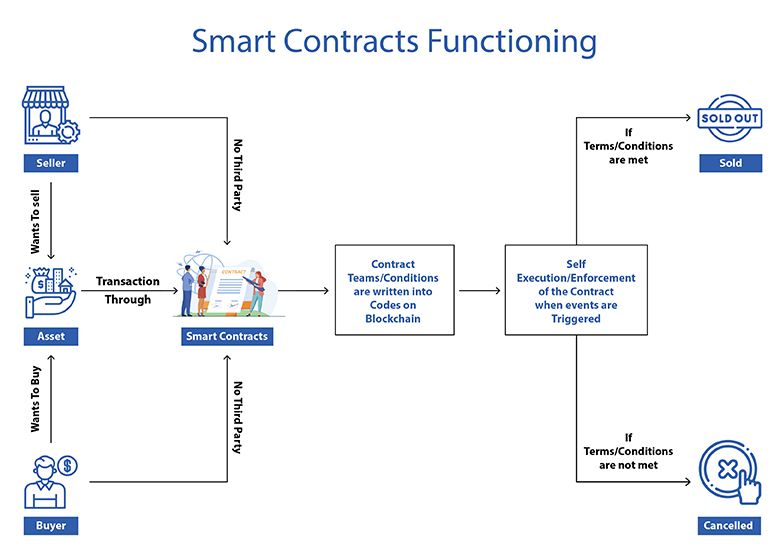
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller directly written into code. These contracts are stored on a blockchain, making them secure, transparent, and irreversible. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers or banks, to enforce the terms of the contract.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart contracts are programmed to automatically execute actions when certain conditions are met. For example, if a buyer purchases a product using a smart contract, the contract will automatically release payment to the seller once the product is delivered. This eliminates the need for manual intervention and ensures that both parties uphold their end of the agreement.
Smart contracts operate on the principle of “if-then” logic. When certain conditions are met, the contract executes the specified actions. This makes smart contracts an efficient and reliable way to conduct transactions without the need for trust between parties.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
There are several benefits to using smart contracts for agreements and transactions. Some of the key benefits include:
Security: Smart contracts are stored on a blockchain, making them secure and resistant to tampering.
Transparency: All transactions conducted through smart contracts are recorded on the blockchain, providing a transparent record of the agreement.
Efficiency: Smart contracts automate the execution of agreements, saving time and reducing the need for manual intervention.
Trustless: Smart contracts eliminate the need for trust between parties, as the terms of the agreement are enforced automatically.
Use Cases for Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have a wide range of use cases across various industries. Some common examples of smart contract applications include:
Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts can be used to track and manage the flow of goods in supply chains, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Real Estate Transactions: Smart contracts can streamline the process of buying and selling properties by automating the transfer of ownership and payment.
Insurance Claims: Smart contracts can automate the verification and payout of insurance claims, making the process faster and more efficient.
Token Sales: Smart contracts are commonly used in token sales and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) to automate the distribution of tokens to investors.
Conclusion
Smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize the way agreements and transactions are executed by eliminating the need for intermediaries and automating the process. By understanding how smart contracts work and their benefits, businesses and individuals can take advantage of this innovative technology to streamline operations and increase efficiency.
Whether you are a tech enthusiast or a business owner, incorporating smart contracts into your operations can provide you with a competitive edge in today’s digital world.